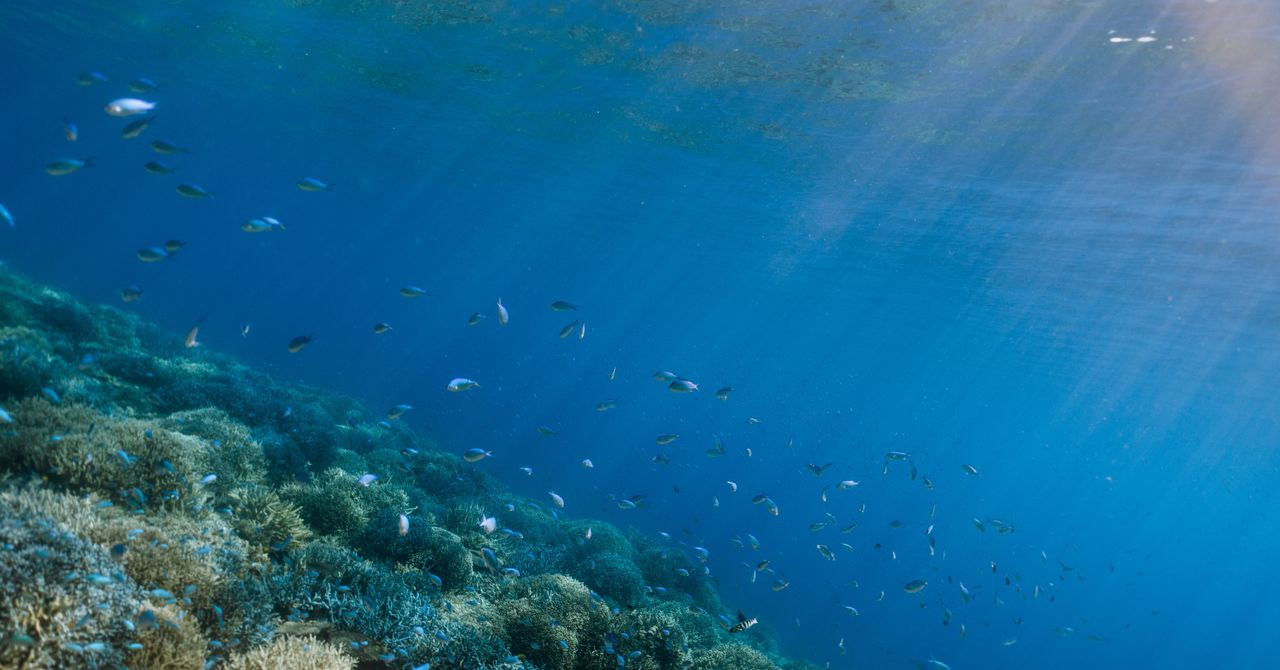
For a living Earth, the oceans are necessary. Not only supply us with food and resources, they also play a big role in maintaining a stable climate: between one quarter to one-third of all coins2 Emited by people, which would otherwise stay in the atmosphere for further intensification of climate change, are captured and stored by the sea.
But the oceans are in trouble. Already confronted by human pressures – including excessive fishing, pollution, growing temperatures and acidification – world sea must see the burden that is placed in the next few decades. This would have huge negative consequences for biodiversity as well as for people around the world.
The International Team, led by the National Center for Analysis and Synthesis of the University of California, Santa Barbara, models that the pressure was placed on the world’s oceans in the future. Their analysis of projects Yes by around 2050. year, cumulative pressure on the oceans could increase 2.2 to 2.6 times compared to today. The fastest increase in influence will appear near the equator, on columns and in coastal areas.
“Our cumulative impact on the oceans, which is already significant, doubles by 2050 – in just 25 years,” Ben Halpern, the marine ecologist and the director of the NCEAS explained in the University statement. “It’s sober. And he’s unexpectedly, and not because the influences will increase – that’s not surprising – but because it will increase so fast.”
Halpern and his team, in cooperation with Nelson Mandela in South Africa, integrated 17 sets from all over the world to create a comprehensive global model to the extent of the impact of human activities on the ocean. Last studies often dealt with the impacts of specific activities in isolation; The current study integrates these activities to the clearer emphasis on the future vision of the marine environment.
What appears is a picture of further deterioration in already very vulnerable areas, such as coastal waters, as well as the rapid spread of the influence over the tall sea, which are relatively stable so far. In equatorial regions, the influence of human activities could increase almost three times between the 2040s and 2050s.
Specific main influences include growing sea temperatures, refusing sea resources due to fishing, growing seabed levels, sheaving seawater (which is the consequence of the co2 Solvement in the sea), and algalic flowers due to the influx of nutrients that invest in the ocean, mainly from the farm. Although these loads are serious in isolation, their combined effects could exceed ecosystem resistance and lead to irreversible losses.
Researchers warn that this cumulative impact will then hit the company, for example, by killing food in tourism and fishing, flooding of low-letter countries and destroying coral reefs that protect the shores of storms and tsunami. There will be direct influences on human resources and the economy, leading to regional economic instability, Halpern said.
Earths in the development and small island nation, they are especially economic to take measure adjustments, despite their often severe dependence on sea resources. Cumulative effects will therefore appear unequable throughout the countries. Ocean change is not just environmental issues; It is a matter related to the stability of the international community as a whole.
However, the projections of this study are only opportunities; Such a future does not have to arrive. Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions for climate change and ocean acidification, systematically manage fishery resources, avoiding coastal pollution, and the preservation of coastal mongoons and wet salts can help alleviate deterioration. There is still a space to minimize the impact.
This story originally appeared Wired Japan And it was translated from Japanese.