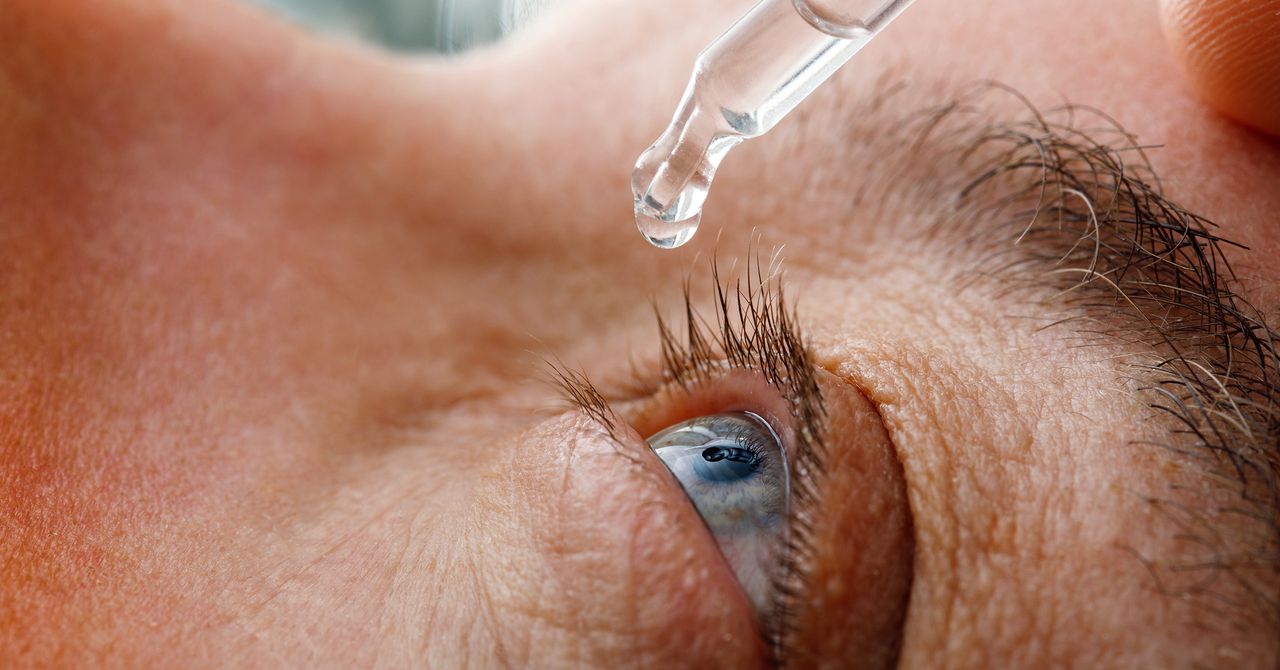
Statistics no Feeling: After 65, most people will fight to visually focus on close-up facilities. You may have seen it among your friends and relatives or even gained it yourself, holding books, magazines, or phone further than your face to try to invest words and pictures in focus. Many of those who are affected begin to use reading glasses. But a new treatment can become available: eye drops.
This deterioration vision is called presbyopia. It is not a disease, but a natural, physiological change caused by aging loss of charming lenses on the front of the eye, which reduces the ability of the eye to change the curvature of the lens to focus. This fixing begins in the middle age and usually stabilizes about 65 years. For people with short-sightedness, or mistake to see distant items, at the beginning of Presbyopia can initially lead to an improved vision compensation for their existing condition. For those with further light or hyperopia, the effects of presbooks often represent earlier than in the rest of the population.
I live with a prespecoach can cause fatigue and headaches, and in rare cases a double vision, but it is generally not concern. But correcting can facilitate daily activities and help maintain good quality of life. Classical correction agents are reading glasses, although in some cases they are decided by the eye surgery – there are laser refractive surgery for rehearsal for reimbursement of lens flexibility. The latter often suggests when there is also some blurring in the lens (cataract).
But recently, researchers work on eye drops that, in different ways, depending on the active ingredient used, improve close to the focus. Two species were approved by the American food and medicine administration: one on the basis of a substance called Aceclidin, others on pilocarpine.
Pilocrapine is a star molecule, with multiple tests of new formulations in progress. It is a natural alkaloid that acts with parts of the nervous system, which has the effect, in the eyes of the Miosa – narrowing the diameter of the pupils – and the contraction of muscles that controls the shape of the lens. The two effects combined improve the elasticity of the objects and the ability to focus on nearby objects.
The recent trial in Argentina tested the fall of the pilocarpin eye in different concentrations (1 percent, 2 percent, 3 percent) in a combination of Diclofenac, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory attack that calms the negative effects of pilocarpas such as irritation and discomfort. (FDA-approved piloca is concentrated in 1.25 percent.)
In a two-year retrospective study of 766 people, an average year 55 years old, researchers found that eye drops enabled most of patients to improve their vision. “Our most significant result showed quick and lasting improvements in sight for all three concentrations,” said the main researcher of Giovanna Benozza when he was research at 43. Congress of the European Society of Cataracts and Surgeon Refraction.