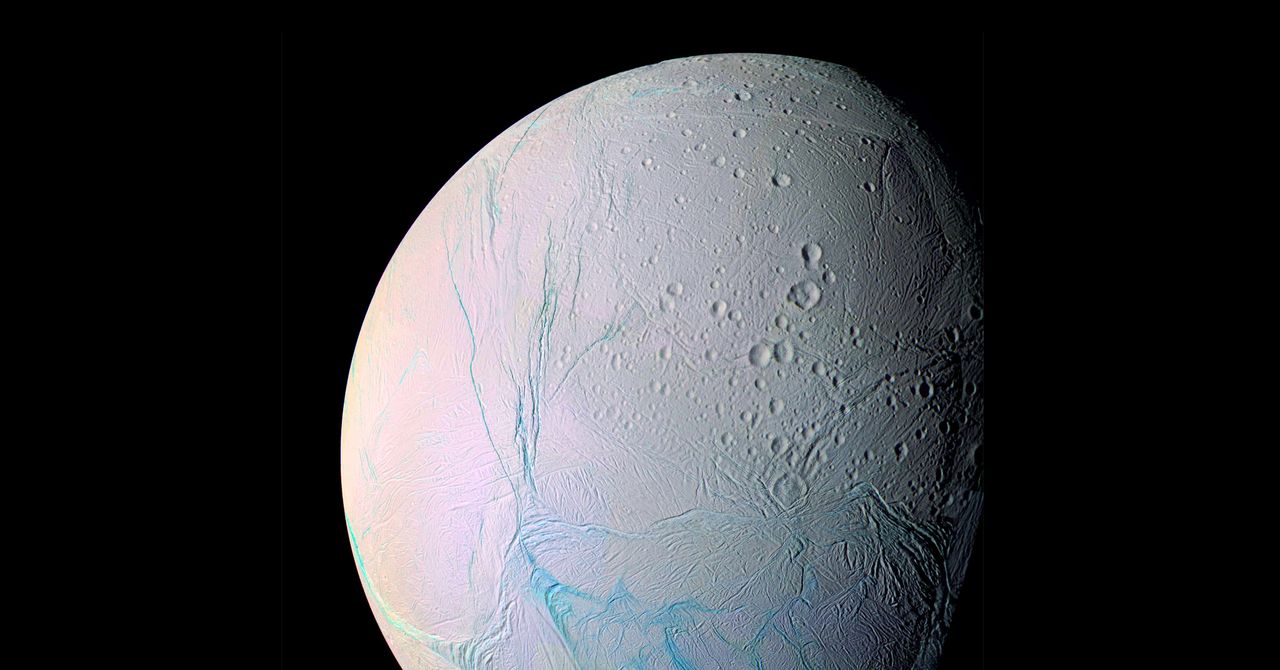
Recent study Enceladus, one of Saturn’s months, revealed several organic compounds that have never been recorded before. The findings were published this month in the astronomy of nature, provide new marks on the inner chemical composition of this icy world, as well as a new hope that you could pound life.
The researchers analyzed data from the Cassini probe, which appeared in 1997. and studied Saturn and his moon to his destruction in 2017. year, Cassini collected data from the icy fragments from the Moon’s underground ocean into space.
Enceladus has been discovered in Saturn’s gravitational withdrawal by 274. It measures a diameter about 500 kilometers, which makes it a planet six-largest satellite. Although this month does not expire for its size, it is significant for its cryonolcanoes on Encladus South Pole, which has expelled water vapor and ice fragments. The plumps of expelled material can be expanded to almost 10,000 kilometers in length, which is more than a distance from Mexico to Patagonia, and some of this material rises into space. The farthest saturn’s main rings – his ring – primarily seems of ice thrown in the enceladus space.
It is believed that this material comes from the saline water chamber below the moon iceberg that is associated with its rocky core. It is possible that chemical reactions take place down, under high pressure and warm.
So far, most chemical analysis of ice from Enceladus was deposited in Saturn’s E ring. But during the fast flying month in 2008. Cassini was sufficient enough to sample freshly thrown fragments from Kriovolcan. New research work reaffirmed this data, confirming the presence of previously discovered organic molecules, as well as the detection of compounds previously undetected.
“Such compounds are of the intermediaries in the synthesis of more complex molecules, which could be potentially biologically relevant. However, these molecules,” Nozair Khawaja, the planetary scientist from Berlin and the leading author of the study, said for Reuters. The discovery significantly expands the range of confirmed organic molecules on encepladus.
The key is that the compounds appeared in freshly thrown particles, suggesting that they were formed within the moon-hidden ocean or in contact with their internal interfaces, not during travel via e-ring or exposure. This increases the hypothesis that the hydrothermal processes below the enSpoladus surface could generate rich organic chemistry. By combining this new research with previous studies, scientists have now found five out of six elements that are necessary for life-carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus and sulfur disincludes satellite material.
Sam alone is not the discovery of life, nor biosignatures – signs of life. However, the research confirms that Enceladus has three basic conditions for life in the form: liquid water, energy source and essential elements and bodies. “Enceladus is, and it should be ranked, as the main target for researching residence and search whether there is life or not,” Khawaja said.
This story originally appeared Wired In Spanish And he was translated from Spanish.